Portal:Spain
Portal maintenance status: (June 2018)
|
The Spain Portal (Bienvenido al portal español)

Spain, formally the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in southwestern Europe, with parts of its territory in the Atlantic Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea and Africa. It is the largest country in Southern Europe and the fourth-most populous European Union member state. Spanning across the majority of the Iberian Peninsula, its territory also includes the Canary Islands in the Atlantic Ocean, the Balearic Islands in the Mediterranean Sea, and the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla in Africa. Peninsular Spain is bordered to the north by France, Andorra, and the Bay of Biscay; to the east and south by the Mediterranean Sea and Gibraltar; and to the west by Portugal and the Atlantic Ocean. Spain's capital and largest city is Madrid, and other major urban areas include Barcelona, Valencia, and Zaragoza.
In early antiquity, the Iberian Peninsula was inhabited by Celts, Iberians, and other pre-Roman peoples. With the Roman conquest of the Iberian Peninsula, the province of Hispania was established. Following the Romanization and Christianization of Hispania, the fall of the Western Roman Empire ushered in the inward migration of tribes from Central Europe, including the Visigoths, who formed the Visigothic Kingdom centred on Toledo. In the early eighth century, most of the peninsula was invaded by the Umayyad Caliphate, and during early Islamic rule, Al-Andalus became a dominant peninsular power centred on Córdoba. Several Christian kingdoms emerged in Northern Iberia, chief among them Asturias, León, Castile, Aragon, Navarre, and Portugal; made an intermittent southward military expansion and repopulation, known as the Reconquista, repelling Islamic rule in Iberia, which culminated with the Christian seizure of the Nasrid Kingdom of Granada in 1492. The dynastic union of the Crown of Castile and the Crown of Aragon in 1479 under the Catholic Monarchs is often considered the de facto unification of Spain as a nation-state. (Full article...)
 Featured article – show another
Featured article – show another
-
Image 1The Oran fatwa was a responsum fatwa, or an Islamic legal opinion, issued in 1502 to address the crisis that occurred when Muslims in the Crown of Castile, in present-day Spain, were forced to convert to Christianity in 1500–1502. It was authored by mufti Ahmad ibn Abi Jum'ah, an Algerian scholar of Islamic law of the Maliki school; the term "Oran fatwa" was applied by modern scholars, due to the word "Al-Wahrani" ("of Oran") that appears in the text as part of the author's name. (Full article...)
-
Image 2

Boletus aereus, commonly known as the dark cep, bronze bolete, or queen bolete, is a highly prized and much sought-after edible mushroom in the family Boletaceae. The bolete is widely consumed in Spain (Basque Country and Navarre), France, Italy, Greece, and generally throughout the Mediterranean. Described in 1789 by French mycologist Pierre Bulliard, it is closely related to several other European boletes, including B. reticulatus, B. pinophilus, and the popular B. edulis. Some populations in North Africa have in the past been classified as a separate species, B. mamorensis, but have been shown to be phylogenetically conspecific to B. aereus and this taxon is now regarded as a synonym. (Full article...) -
Image 3
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Italy and Iberia, but also on the islands of Sicily and Sardinia and, towards the end of the war, in North Africa. After immense materiel and human losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were once again defeated. Macedonia, Syracuse and several Numidian kingdoms were drawn into the fighting, and Iberian and Gallic forces fought on both sides. There were three main military theatres during the war: Italy, where Hannibal defeated the Roman legions repeatedly, with occasional subsidiary campaigns in Sicily, Sardinia and Greece; Iberia, where Hasdrubal, a younger brother of Hannibal, defended the Carthaginian colonial cities with mixed success before moving into Italy; and Africa, where Rome finally won the war. (Full article...) -
Image 4The Nyon Conference was a diplomatic conference held in Nyon, Switzerland, in September 1937 to address attacks on international shipping in the Mediterranean Sea during the Spanish Civil War. The conference was convened in part because Italy had been carrying out unrestricted submarine warfare, although the final conference agreement did not accuse Italy directly; instead, the attacks were referred to as "piracy" by an unidentified body. Italy was not officially at war, nor did any submarine identify itself. The conference was designed to strengthen non-intervention in the Spanish Civil War. The United Kingdom and France led the conference, which was also attended by Bulgaria, Egypt, Greece, Romania, Turkey, the Soviet Union and Yugoslavia. (Full article...)
-
Image 5
The First Punic War (264–241 BC) was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and greatest naval war of antiquity, the two powers struggled for supremacy. The war was fought primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters, and also in North Africa. After immense losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were defeated and Rome gained territory from Carthage. (Full article...) -
Image 6Battle of Chiclana, 5 March 1811, Louis-François Lejeune
The Battle of Barrosa (Chiclana, 5 March 1811, also known as the Battle of Chiclana or Battle of Cerro del Puerco) was part of an unsuccessful manoeuvre by an Anglo-Iberian force to break the French siege of Cádiz during the Peninsular War. During the battle, a single British division defeated two French divisions and captured a regimental eagle. (Full article...) -
Image 7

North View of Gibraltar from Spanish Lines by John Mace (1782)
The history of Gibraltar, a small peninsula on the southern Iberian coast near the entrance of the Mediterranean Sea, spans over 2,900 years. The peninsula has evolved from a place of reverence in ancient times into "one of the most densely fortified and fought-over places in Europe", as one historian has put it. Gibraltar's location has given it an outsized significance in the history of Europe and its fortified town, established in the Middle Ages, has hosted garrisons that sustained numerous sieges and battles over the centuries. (Full article...) -
Image 8
Alfonso XIII was the second of three España-class dreadnought battleships built in the 1910s for the Spanish Navy. Named after King Alfonso XIII of Spain, the ship was not completed until 1915 owing to a shortage of materials that resulted from the start of World War I the previous year. The España class was ordered as part of a naval construction program to rebuild the fleet after the losses of the Spanish–American War; the program began in the context of closer Spanish relations with Britain and France. The ships were armed with a main battery of eight 305 mm (12 in) guns and were intended to support the French Navy in the event of a major European war. (Full article...) -
Image 9View of Badajoz, across the Guadiana river from the foothills of the San Cristóbal heights, by Eugène-Ferdinand Buttura
The Battle of the Gebora took place during the Peninsular War between Spanish and French armies on 19 February 1811, northwest of Badajoz, Spain. An outnumbered French force routed and nearly destroyed the Spanish Army of Extremadura. (Full article...) -
Image 10

An M48 Patton tank of the Spanish Army on display at the El Goloso Museum of Armored Vehicles in October 2007.
Tanks in the Spanish Army have over 90 years of history, from the French Renault FTs first delivered in 1919 to the Leopard 2 and B1 Centauro models of the early 21st century. The Spanish FTs took part in combat during the Rif War and participated in the first amphibious landing with tanks in history, at Alhucemas. In 1925, the Spanish Army began to undertake a program to develop and produce a Spanish tank, an upgraded version of the Renault FT, called the Trubia A4. Although the prototype performed well during testing, the tank was never put into mass production. Spain also experimented with the Italian Fiat 3000, acquiring one tank in 1925, and with another indigenous tank program called the Landesa. However, none of these evolved into a major armor program, and as a result the FT remained the most important tank, in numbers, in the Spanish Army until the beginning of the Spanish Civil War. (Full article...) -
Image 11

Hieronymus Bosch, The Garden of Earthly Delights, oil on oak panels, 205.5 cm × 384.9 cm (81 in × 152 in), Museo del Prado, Madrid
The Garden of Earthly Delights (Dutch: De tuin der lusten, lit. 'The garden of lusts') is the modern title given to a triptych oil painting on oak panel painted by the Early Netherlandish master Hieronymus Bosch, between 1490 and 1510, when Bosch was between 40 and 60 years old. It has been housed in the Museo del Prado in Madrid, Spain since 1939. (Full article...) -
Image 12
The AMX-30E (E stands for España, Spanish for Spain) is a Spanish main battle tank based on France's AMX-30. Although originally the Spanish government sought to procure the German Leopard 1, the AMX-30 was ultimately awarded the contract due to its lower price and the ability to manufacture it in Spain. 280 units were manufactured by Santa Bárbara Sistemas for the Spanish Army, between 1974 and 1983. (Full article...) -
Image 13The Colossus of Rhodes is a 1954 oil painting by the Spanish surrealist Salvador Dalí. It is one of a series of seven paintings he created for the 1956 film Seven Wonders of the World, each depicting one of the wonders. The work shows the Colossus of Rhodes, the ancient statue of the Greek titan-god of the sun, Helios. The painting was not used for the film and was donated to the Kunstmuseum Bern in 1981, where it remains. (Full article...)
-
Image 14The Mercenary War, also known as the Truceless War, was a mutiny by troops that were employed by Carthage at the end of the First Punic War (264–241 BC), supported by uprisings of African settlements revolting against Carthaginian control. It lasted from 241 to late 238 or early 237 BC and ended with Carthage suppressing both the mutiny and the revolt. (Full article...)
-
Image 15Hurricane Leslie near peak intensity southwest of the Azores on 11 October
Hurricane Leslie (known as Storm Leslie or Cyclone Leslie while extratropical) was the strongest cyclone of tropical origin to strike the Iberian Peninsula since 1842. A large, long-lived, and very erratic tropical cyclone, Leslie was the twelfth named storm and sixth hurricane of the 2018 Atlantic hurricane season. The storm had a non-tropical origin, developing from an extratropical cyclone that was situated over the northern Atlantic on 22 September. The low quickly acquired subtropical characteristics and was classified as Subtropical Storm Leslie on the following day. The cyclone meandered over the northern Atlantic and gradually weakened, before merging with a frontal system on 25 September, which later intensified into a powerful hurricane-force extratropical low over the northern Atlantic. (Full article...) -
Image 16Muhammad III (Arabic: محمد الثالث; 15 August 1257 – 21 January 1314) was the ruler of the Emirate of Granada in Al-Andalus on the Iberian Peninsula from 8 April 1302 until 14 March 1309, and a member of the Nasrid dynasty. He ascended the Granadan throne after the death of his father Muhammad II, which according to rumours, was caused by Muhammad III poisoning him. He had the reputation of being both cultured and cruel. Later in his life, he became visually impaired—which caused him to be absent from many government activities and to rely on high officials, especially the powerful Vizier Ibn al-Hakim al-Rundi. (Full article...)
-
Image 17

Plate 34: Por una navaja (For a clasp knife). A garroted priest grasps a crucifix in his hands. Pinned to his chest is a description of the crime for which he was killed—possession of a knife.
The Disasters of War (Spanish: Los desastres de la guerra) is a series of 82 prints created between 1810 and 1820 by the Spanish painter and printmaker Francisco Goya (1746–1828). Although Goya did not make known his intention when creating the plates, art historians view them as a visual protest against the violence of the 1808 Dos de Mayo Uprising, the subsequent cruel war that ended in Spanish victory in the Peninsular War of 1808–1814 and the setbacks to the liberal cause following the restoration of the Bourbon monarchy in 1814. During the conflicts between Napoleon's French Empire and Spain, Goya retained his position as first court painter to the Spanish crown and continued to produce portraits of the Spanish and French rulers. Although deeply affected by the war, he kept private his thoughts on the art he produced in response to the conflict and its aftermath. (Full article...) -
Image 18The Battle of Pavia, by an unknown Flemish artist
The Italian War of 1521–1526, sometimes known as the Four Years' War, (French: Sixième guerre d'Italie) was a part of the Italian Wars. The war pitted Francis I of France and the Republic of Venice against the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V, Henry VIII of England, and the Papal States. It arose from animosity over the election of Charles as Emperor in 1519–1520 and from Pope Leo X's need to ally with Charles against Martin Luther. (Full article...) -
Image 19Spanish Leopard 2E in Zaragoza, June 2008
The Leopardo 2E or Leopard 2A6E (E stands for España (Spanish for 'Spain')) is a variant of the German Leopard 2 main battle tank (specifically the Leopard 2A6 variant), tailored to the requirements of the Spanish army, which acquired it as part of an armament modernization program named Programa Coraza, or Program Cuirass. The acquisition program for the Leopard 2E began in 1994, five years after the cancellation of the Lince tank program that culminated in an agreement to transfer 108 Leopard 2A4s to the Spanish army in 1998 and started the local production of the Leopard 2E in December 2002. Despite postponement of production owing to the 2003 merger between Santa Bárbara Sistemas and General Dynamics, and continued manufacturing issues between 2006 and 2007, 219 Leopard 2Es have been delivered to the Spanish army. (Full article...) -
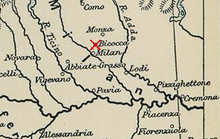
Image 20Lombardy in 1522. The location of the battle is marked.
The Battle of Bicocca or La Bicocca (Italian: Battaglia della Bicocca) was fought on 27 April 1522, during the Italian War of 1521–26. A combined French and Venetian force under Odet de Foix, Vicomte de Lautrec, was decisively defeated by an Imperial–Spanish and Papal army under the overall command of Prospero Colonna. Lautrec then withdrew from Lombardy, leaving the Duchy of Milan in Imperial hands. (Full article...) -
Image 21Dinar minted in Yusuf I's name
Abu al-Hajjaj Yusuf ibn Ismail (Arabic: أبو الحجاج يوسف بن إسماعيل; 29 June 1318 – 19 October 1354), known by the regnal name al-Muayyad billah (المؤيد بالله, "He who is aided by God"), was the seventh Nasrid ruler of the Emirate of Granada on the Iberian Peninsula. The third son of Ismail I (r. 1314–1322), he was Sultan between 1333 and 1354, after his brother Muhammad IV (r. 1325–1333) was assassinated. (Full article...) -
Image 22Conquistador Pedro de Alvarado led the initial efforts to conquer Guatemala.
In a protracted conflict during the Spanish colonization of the Americas, Spanish colonisers gradually incorporated the territory that became the modern country of Guatemala into the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain. Before the conquest, this territory contained a number of competing Mesoamerican kingdoms, the majority of which were Maya. Many conquistadors viewed the Maya as "infidels" who needed to be forcefully converted and pacified, disregarding the achievements of their civilization. The first contact between the Maya and European explorers came in the early 16th century when a Spanish ship sailing from Panama to Santo Domingo was wrecked on the east coast of the Yucatán Peninsula in 1511. Several Spanish expeditions followed in 1517 and 1519, making landfall on various parts of the Yucatán coast. The Spanish conquest of the Maya was a prolonged affair; the Maya kingdoms resisted integration into the Spanish Empire with such tenacity that their defeat took almost two centuries. (Full article...) -
Image 23Northern Italy in 1494; by the start of the war in 1508, Louis XII had expelled the Sforza from the Duchy of Milan and added its territory to France.
The War of the League of Cambrai, sometimes known as the War of the Holy League and several other names, was fought from February 1508 to December 1516 as part of the Italian Wars of 1494–1559. The main participants of the war, who fought for its entire duration, were France, the Papal States, and the Republic of Venice; they were joined at various times by nearly every significant power in Western Europe, including Spain, the Holy Roman Empire, England, the Duchy of Milan, the Republic of Florence, the Duchy of Ferrara, and the Swiss. (Full article...) -
Image 24
Verdeja was the name of a series of light tanks developed in Spain between 1938 and 1954 in an attempt to replace German Panzer I and Soviet T-26 tanks in Spanish service. (Full article...) -
Image 25A Wehrmacht Panzerkampfwagen I Ausf. A light tank on display at the Deutsches Panzermuseum Munster in Munster, Germany.
The Panzer I was a light tank produced by Nazi Germany in the 1930s. Its name is short for Panzerkampfwagen I (German for "armored fighting vehicle mark I"), abbreviated as PzKpfw I. The tank's official German ordnance inventory designation was Sd.Kfz. 101 ("special purpose vehicle 101"). (Full article...)
Selected biography
Lope de Aguirre (c. 1510 – 27 October 1561) was a Spanish Basque conquistador in South America. Sent, along other rebellious settlers, to an impossible mission in search of the mythical Eldorado in the Amazon river, he eventually became their leader and rebelled against Philip II, being finally defeated and slain. Aguirre was born circa 1510 in Araotz Valley, in the Basque province of Guipúzcoa, part of the kingdom of Castile. (Today, Araotz belongs to the near municipality of Oñati, in northern Spain.) He was the son of a nobleman, with some culture, possibly from a family of court clerks. Aguirre was in his twenties and living in Seville when Hernándo Pizarro returned from Peru and brought back the treasures of the Incas, inspiring Aguirre to follow in his footsteps.
Aguirre probably enlisted himself in an expedition of 250 men chosen under Rodrigo Buran. He arrived in Peru in 1536 or 1537. In Cuzco, among other activities, Aguirre was responsible for the training of stallions. As a conquistador, however, he soon became infamous for his violence, cruelty and sedition. In 1544, Aguirre was at the side of Peru's first viceroy, Blasco Núñez Vela, who had arrived from Spain with orders to implement the New Laws, suppress the Encomiendas, and liberate the natives.
Selected picture
-
Image 1Photograph: Diego DelsoMoros is a municipality in the province of Zaragoza, Spain. Located in the Sistema Ibérico mountain range, the village lies on a hill, with the church and former town hall at the top, the residences in the middle, and the sheep pens at the bottom. The population of Moros has been steadily decreasing in recent decades, and was 478 in 2006.
-
Image 2Photograph: Diego DelsoThe Assut de l'Or Bridge is a white single-pylon cable-stayed bridge in the City of Arts and Sciences, Valencia, Spain. Completed in 2008, it was designed by Valencian architect and civil engineer Santiago Calatrava as a variant of his cantilever spar cable-stayed bridge in Seville.
-
Image 3

Seville Cathedral. Credit: Seville Tourism Bureau
The Cathedral of Seville, formally Catedral de Santa María de la Sede (Cathedral of Saint Mary of the See) was begun in 1402, with construction continuing into the 16th century. It is the largest of all Roman Catholic cathedrals (Saint Peter's Basilica not being a cathedral) and also the largest Medieval Gothic religious building, in terms of both area and volume. -
Image 4
Cala Figuera Credit: BuzzWoof
The harbor entrance to Cala Figuera, a district of Mallorca in the Balearic Islands. The town is located approximately 60 kilometers north of Palma de Mallorca. The earliest records of the town date back to 1306, although houses were not built on the land until the early 19th century. -
Image 5The peaks of the Central Massif overlook the village of Sotres in Cabrales, located in the Picos de Europa, a mountain range in northern Spain forming part of the Cantabrian Mountains. The name (literally: "Peaks of Europe") is believed to derive from being the first European landforms visible to mariners arriving from the Americas.
-
Image 6Artist: UnknownFerdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor, is represented in this anonymous portrait as a young archduke in his native Spain. He left Spain in his early twenties, to start his life as future King of the Romans and successor to his grandfather, Maximilian I. His older brother Charles eventually succeeded as Holy Roman Emperor, but Ferdinand was elected after Charles's abdication. Philip, Charles's son, inherited Spain and became King Philip II of Spain. Ferdinand ruled between 1558 and 1564, for nearly six years.
-
Image 7
The Temple of Debod. Credit: OsvaldoGagoThe Temple of Debod is an ancient Egyptian temple which has been rebuilt in Madrid, Spain. The temple was built in southern Egypt, very close to the first cataract of the Nile and to the great religious center dedicated to the goddess Isis, in Philae. -
Image 8Photograph credit: Biblioteca Nacional de EspañaAna Santos Aramburo (born 1957) has been the director of the National Library of Spain since February 2013. Having received a degree in geography and history from the University of Zaragoza in Spain, she has spent much of her career working at the Complutense University of Madrid, first at the library of the Faculty of Economics and Business Sciences, and later serving as deputy director of the university library. Later she served as Director of the Historical Library Marquis of Valdecilla, General Director of Libraries and Archives of the City of Madrid, and Director of Cultural Action at the National Library. This photograph of Santos shows her at the headquarters of the National Library of Spain in Madrid.
-
Image 9Gaspar de Guzmán, Count-Duke of Olivares (1587–1645) was a Spanish royal favourite of Philip IV and minister. As prime minister from 1621 to 1643, he over-exerted Spain in foreign affairs and unsuccessfully attempted domestic reform. His policies of committing Spain to recapture the Dutch Republic led to his major involvement in the Thirty Years War. This portrait was completed in 1634, with its composition referring to Olivares' military leadership in the service of King Philip.
-
Image 10Painting credit: Francisco GoyaCharles IV of Spain and His Family is a portrait of the royal family of Spain painted by Francisco Goya in 1800 and 1801. King Charles IV, his wife Maria Luisa of Parma, and his children and relatives are dressed in the height of contemporary fashion, lavishly adorned with jewelry and the sashes of the order of Charles III. The artist does not attempt to flatter the family; instead the group portrait is unflinchingly realist, both in detail and tone. The artist, seated at his easel, is visible in the background. The painting is in the collection of the Museo del Prado in Madrid.
-
Image 11Image: Royal Household of Spain; Restoration: Lise BroerA Grant of Arms by Philip II of Spain to Alonso de Mesa and Hernando de Mesa, signed 25 November 1566. In Spanish heraldry, coats of arms were granted based almost entirely on military service, which made it possible for commoners to join the ranks of the Spanish nobility. Also unique to Spain was that titles could be inherited through females and via illegitimacy.
-
Image 12Painting: Francisco GoyaThe Third of May 1808 is a painting completed in 1814 by the Spanish master Francisco Goya, now in the Museo del Prado, Madrid. Along with its companion piece of the same size, The Second of May 1808 (or The Charge of the Mamelukes), it was commissioned by the provisional government of Spain at Goya's suggestion. Goya sought to commemorate Spanish resistance to Napoleon's armies during the Peninsular War.
-
Image 13Banknote: Bank of SpainThe Spanish peseta is a former currency of Spain and, alongside the French franc, a former de facto currency in Andorra. It was introduced in 1868, replacing the peso, at a time when Spain was considering joining the Latin Monetary Union. Spain joined the euro in 1999, and the peseta was replaced by euro notes and coins in 2002.
This picture shows a 1000 peseta banknote from 1957. The obverse depicts the Catholic Monarchs while the reverse shows the coat of arms of Spain. -
Image 15

A statue showing Christopher Columbus Credit: Luis GarcíaA statue showing Christopher Columbus and Queen Isabella, the statue was made in 1885. -
Image 16Coin design credit: Duchy of ParmaThe doubloon was a Spanish gold coin worth two escudos or 32 reales weighing 6.867 grams (0.221 troy ounces), introduced in 1537. It became the model for several other gold coins issued in Europe, including this 1626 two-doppie gold coin issued in Piacenza in northern Italy by the Duchy of Parma, depicting Odoardo Farnese, Duke of Parma, on the obverse. The coin is part of the National Numismatic Collection at the National Museum of American History.
-
Image 17Painting: Marià FortunyThe Spanish Wedding is an oil on panel painting by Marià Fortuny completed over a two-year period ending in 1870. It depicts the signing of a wedding contract in 18th century Spain and was influenced heavily by the works of Francisco Goya, whom the artist admired. It is currently exhibited at the National Art Museum of Catalonia.
-
Image 18Smoke coming from Madrid Barajas International Airport after the 2006 Madrid Barajas International Airport bombing. The terrorist incident occurred on the morning of December 30, 2006, when an explosion took place in the carpark building attached to Terminal 4 of the airport.
-
Image 20
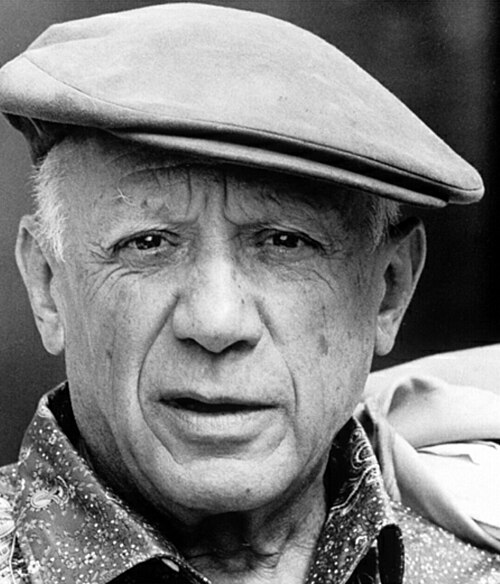

Pablo Picasso Credit: TyreniusPablo Picasso (October 25, 1881 — April 8, 1973) was an artist and sculptor. Picasso was born in Málaga, Spain. This image was taken of him in 1962, eleven years before his death. -
Image 21Photo credit: David IliffThe Tagus River, seen here passing through the World Heritage listed city of Toledo, Spain. It is the longest river on the Iberian Peninsula at 1,038 kilometres (645 mi). It begins its journey in the Albarracín mountains in Spain, and follows a very constricted course for much of its length before reaching the Atlantic Ocean in Portugal.
-
Image 22Architecture credit: José Grases Riera; photographed by Carlos DelgadoThe Monument to Alfonso XII is located in Buen Retiro Park (El Retiro) in Madrid, Spain. Measuring 30 m (98 ft) high, 86 m (282 ft) long, and 58 m (190 ft) wide, it has at its center an equestrian statue of King Alfonso XII, cast in bronze by the Spanish sculptor Mariano Benlliure in 1904. The monument is situated on the eastern edge of an artificial lake near the center of the park and was inaugurated on 6 June 1922.
Did you know...
- ... that some California schoolchildren build dioramas when learning about their state's Spanish missions?
- ... that in 1976, Carmen Valero became the first female track and field athlete to represent Spain at the Olympics?
- ... that after fleeing the Spanish Civil War to Venezuela, Spanish anarchist Concha Liaño became a supporter of Hugo Chávez?
- ... that Swiss athlete Clara Thalmann arrived in Barcelona to compete in the People's Olympiad but ended up fighting in the Spanish Civil War?
- ... that Irish International Brigader Tommy Wood had only been in Spain for 18 days when he was killed at the Battle of Lopera during the Spanish Civil War?
- ... that Spanish mystic Marina de Escobar founded a convent but never joined one?
 Good article – show another
Good article – show another
-
Image 1Pic-Nic was a Spanish teenage folk-pop and sunshine pop band formed in Barcelona in the mid-to-late 1960s, composed of lead singer Jeanette, guitarists Toti Soler and Al Cárdenas, drummer Jordi Barangé and bassist Isidoro "Doro" de Montaberry. Although keyboardist Jordi Sabatés is often mentioned as a member of the band, he does not appear on any of the group's releases, having joined after their only published recording sessions had taken place. Pic-Nic was the successor to the short-lived group Brenner's Folk, originally founded by German-Venezuelan brothers Haakon and Vytas Brenner together with Soler, Barangé and Jeanette, an English girl who had recently moved to Spain after being raised in the United States. After releasing a four-song extended play for the label Edigsa in 1966, the Brenner brothers left the band, being replaced by Cárdenas and de Montaberry. (Full article...)
-
Image 2"Te Lo Agradezco, Pero No" (English: "Thank you, but no") is a song recorded by Spanish singer Alejandro Sanz and Colombian singer Shakira, for Sanz's eighth studio album El Tren de los Momentos (2006). It was released as the second single from the record in December 2006 by Warner Music Latina. The track was written by Sanz, while production was handled by him along with Lulo Pérez. "Te Lo Agradezco, Pero No" is the second duet recorded by the two singers, following "La Tortura" for Shakira's album Fijación Oral Vol. 1 (2005). The song came about after she approached Sanz, telling him that she wanted to collaborate on something different from her own material. (Full article...)
-
Image 3The States' army in Noordhorn defeated by Verdugo, 1581. Simon Frisius, 1613–1615.
The Battle of Noordhorn, fought on 30 September 1581, was a pitched battle of the Dutch Revolt, fought between a Spanish army commanded by Colonel Francisco Verdugo – consisting of Walloon, German, Spanish, and Albanian soldiers – and a Dutch States rebel army under the Englishman John Norreys – comprising English, Scottish, Dutch, and Walloon troops – in the province of Groningen. In 1580, the Dutch stadtholder of Groningen, George van Lalaing, Count of Rennenberg, had shifted its allegiance from the Dutch to the Spanish side. This opened a new front at the back door of the Dutch Republic, forcing the States-General to dispatch forces to the north. That year the Dutch, under the leadership of John Norreys, succeeded in relieving the town of Steenwijk. In July 1581, Rennenberg died and was replaced by the Spaniard Francisco Verdugo, whose arrival in Groningen with reinforcements changed the situation. On 30 September Verdugo forced Norreys to give battle using a strategy of attrition. (Full article...) -
Image 4
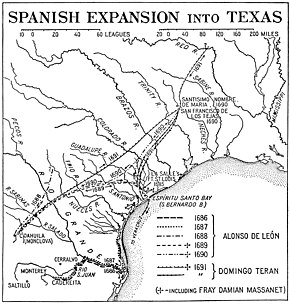
Trails taken by Spanish explorers from Mexico into Texas.
Spanish Texas was one of the interior provinces of the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain from 1519 until 1821. Spain claimed ownership of the region in 1519. Slave raids by Spaniards into what became Texas began in the 16th century and created an atmosphere of antagonism with Native Americans (Indians) which would cause endless difficulties for the Spanish in the future. Spain did not attempt to establish a permanent presence until after France established the colony of Fort Saint Louis in 1685. In 1688, the French colony failed due to internal dissention and attacks by the Karankawa Indians. In 1690, responding to fear of French encroachment, Spanish explorer Alonso de León escorted several Catholic missionaries to east Texas, where they established the first mission in Texas. That attempt to establish a Spanish colony failed due to the hostility of the Caddo Indians. (Full article...) -
Image 5"Rhythm Divine" is a song by Spanish singer Enrique Iglesias from his fourth studio album, Enrique (1999). The song was written by Paul Barry and Mark Taylor with Taylor and Brian Rawling handling its production. It is a dance-pop rhythmic romantic ballad that mixes with Latin and Mediterranean music. Lyrically, Iglesias asks the listener if they can hear the rhythm, and one music journalist compared it to USA for Africa's "We Are the World" (1985). A Spanish-language translation of the song titled "Ritmo Total" was also recorded and features additional lyrical contributions by Rafael Pérez-Botija. (Full article...)
-
Image 6Picture by Johann Jakob Wick illustrating his report about the Battle of Zutphen, published on 12 October 1586
The Battle of Zutphen was fought on 22 September 1586, near the village of Warnsveld and the town of Zutphen, the Netherlands, during the Eighty Years' War. It was fought between the forces of the United Provinces of the Netherlands, aided by the English, against the Spanish. In 1585, England signed the Treaty of Nonsuch with the States-General of the Netherlands and formally entered the war against Spain. Robert Dudley, Earl of Leicester, was appointed as the Governor-General of the Netherlands and sent there in command of an English army to support the Dutch rebels. When Alessandro Farnese, Duke of Parma and commander of the Spanish Army of Flanders, besieged the town of Rheinberg during the Cologne War, Leicester, in turn, besieged the town of Zutphen, in the province of Gelderland and on the eastern bank of the river IJssel. (Full article...) -
Image 7
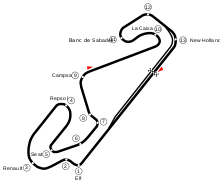
The 2000 Spanish Grand Prix (formally the XLII Gran Premio Marlboro de España) was a Formula One motor race held on 7 May 2000 at the Circuit de Catalunya, in Montmeló, Catalonia, Spain with approximately 79,000 spectators. It was the fifth round of the 2000 Formula One World Championship and the 42nd Spanish Grand Prix. Mika Häkkinen of McLaren won the 65-lap race after starting second. His teammate David Coulthard finished second, with Ferrari's Rubens Barrichello third. (Full article...) -
Image 8Click an image to load the appropriate article.
Left to right, top to bottom:
Battles of Malta, 15 July 1798, the Nile, 18 August 1798, the Malta Convoy, 31 March 1800
The Mediterranean campaign of 1798 was a series of major naval operations surrounding a French expeditionary force sent to Egypt under Napoleon Bonaparte during the French Revolutionary Wars. The French Republic sought to capture Egypt as the first stage in an effort to threaten British India and support Tipu Sultan, and thus force Great Britain to make peace. Departing Toulon in May 1798 with over 40,000 troops and hundreds of ships, Bonaparte's fleet sailed southeastwards across the Mediterranean Sea. They were followed by a small British squadron under Rear-Admiral Sir Horatio Nelson, later reinforced to 13 ships of the line, whose pursuit was hampered by a lack of scouting frigates and reliable information. Bonaparte's first target was the island of Malta, which was under the government of the Knights of St. John and theoretically granted its owner control of the Central Mediterranean. Bonaparte's forces landed on the island and rapidly overwhelmed the defenders, securing the port city of Valletta before continuing to Egypt. When Nelson learned of the French capture of the island, he guessed the French target to be Egypt and sailed for Alexandria, but passed the French during the night of 22 June without discovering them and arrived off Egypt first. (Full article...) -
Image 9
Clara Thalmann (née Ensner; 24 September 1908 – 24 January 1987) was a Swiss journalist, athlete and militiawoman, who fought during the Spanish Civil War. (Full article...) -
Image 10

Bartolomé de las Casas, OP (US: /lɑːs ˈkɑːsəs/ lahss KAH-səss; Spanish: [baɾtoloˈme ðe las ˈkasas] ⓘ; 11 November 1484 – 18 July 1566) was a Spanish clergyman, writer, and activist best known for his work as an historian and social reformer. He arrived in Hispaniola as a layman, then became a Dominican friar. He was appointed as the first resident Bishop of Chiapas, and the first officially appointed "Protector of the Indians". His extensive writings, the most famous being A Short Account of the Destruction of the Indies and Historia de Las Indias, chronicle the first decades of colonization of the Caribbean islands. He described the atrocities committed by the colonizers against the indigenous peoples. (Full article...) -
Image 11"Si Tú Te Vas" (English: "If You Go Away") is a song by Spanish singer Enrique Iglesias from his 1995 eponymous debut studio album. The song was co-written by Iglesias when he was 16 and his friend Roberto Morales with Rafael Pérez-Botija handling its production. It was released as the lead single from the album in October 1995. Iglesias recorded a demo of the song which was accepted by Guillermo Santiso, the president of Fonovisa Records, which led to Iglesias signing on with the company. A pop ballad, the song is about a man inspired by love and is afraid of a farewell. A music video for the song was filmed in New York and led to Iglesias being nominated for Best New Artist at the 1996 MTV Latino Awards. (Full article...)
-
Image 12
The Alconétar Bridge (Spanish: Puente de Alconétar), also known as Puente de Mantible, was a Roman segmental arch bridge in the Extremadura region, Spain. The ancient structure, which featured flattened arches with a span-to-rise ratio of 4–5:1, is one of the earliest of its kind. Due to its design, it is assumed that the bridge was erected in the early 2nd century AD by the emperors Trajan or Hadrian, possibly under the guidance of Apollodorus of Damascus, the most famous architect of the time. (Full article...) -
Image 13A denarius of Charlemagne dated c. 812–814 with the inscription KAROLVS IMP AVG
(Karolus Imperator Augustus)
Charlemagne (/ˈʃɑːrləmeɪn, ˌʃɑːrləˈmeɪn/ SHAR-lə-mayn, -MAYN; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and Emperor, of what is now known as the Carolingian Empire, from 800, holding these titles until his death in 814. He united most of Western and Central Europe and was the first recognised emperor to rule in the west after the fall of the Western Roman Empire, approximately three centuries earlier. Charlemagne's reign was marked by political and social changes that had lasting impact on Europe throughout the Middle Ages. (Full article...) -
Image 14A collage of photos taken of Agotes in Bozate [es] at the beginning of the 20th Century
The Cagots (pronounced [ka.ɡo]) were a persecuted minority who lived in the west of France and northern Spain: the Navarrese Pyrenees, Basque provinces, Béarn, Aragón, Gascony and Brittany. Evidence of the group exists as far back as 1000 CE. The name they were known by varied across the regions where they lived. (Full article...) -
Image 15The 1957 Latin Cup (Spanish: Copa Latina de 1957) was the eighth and final edition of the annual Latin Cup. It was contested by the domestic league champions the Southwest European nations of France, Italy, Portugal, and Spain. The clubs which competed in the tournament were AS Saint-Étienne, AC Milan, SL Benfica, and Real Madrid CF. (Full article...)
-
Image 16

Elections to Spain's legislature, the Cortes Generales, were held on 19 November 1933 for all 473 seats in the unicameral Cortes of the Second Spanish Republic. Since the previous elections of 1931, a new constitution had been ratified, and the franchise extended to more than six million women. The governing Republican-Socialist coalition had fallen apart, with the Radical Republican Party beginning to support a newly united political right. (Full article...) -
Image 17Tristan and Isolde (Death), 1910, 160 by 240 cm (63 by 94 in) (Bilbao Fine Arts Museum)
Tristan and Isolde (Spanish: Tristán e Isolda) is the title of two oil paintings by the Spanish artist Rogelio de Egusquiza. Both works are based on the opera Tristan und Isolde by the German composer Richard Wagner, whom Egusquiza idolised. The first painting, subtitled Death and also known as La mort d'Isolde (The Death of Isolde), was completed in 1910 and depicts Isolde's "Liebestod", as she collapses in death upon the lifeless body of Tristan. The second painting, subtitled Life, was completed two years later and depicts the lovers embracing in the night, a scene from the second act of Wagner's opera. (Full article...) -
Image 18
The Monbar Hotel attack was carried out by the Grupos Antiterroristas de Liberación (GAL), a Spanish state-sponsored death squad, on 25 September 1985 in Bayonne, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, France. The targets were four members of the Basque separatist terrorist group Euskadi Ta Askatasuna (ETA), whom the Spanish government believed to be senior figures in the organization, itself proscribed as a terrorist group in Spain and France. All four people were killed, with a fifth person, apparently unconnected to ETA, injured in the shooting. This represented the deadliest attack carried out by the GAL. Although two of the participants were apprehended shortly after the shooting, controversy surrounded the possible involvement of senior figures in the Spanish police. (Full article...) -
Image 19Statue of Averroes in Córdoba, Spain
Ibn Rushd (Arabic: ابن رشد; full name in Arabic: أبو الوليد محمد بن أحمد بن رشد, romanized: Abū al-Walīd Muḥammad ibn Aḥmad ibn Rushd; 14 April 1126 – 11 December 1198), often Latinized as Averroes (English: /əˈvɛroʊiːz/), was an Andalusian polymath and jurist who wrote about many subjects, including philosophy, theology, medicine, astronomy, physics, psychology, mathematics, Islamic jurisprudence and law, and linguistics. The author of more than 100 books and treatises, his philosophical works include numerous commentaries on Aristotle, for which he was known in the Western world as The Commentator and Father of Rationalism. (Full article...) -
Image 20

The 2016 Spanish Grand Prix (formally known as the Formula 1 Gran Premio de España Pirelli 2016) was a Formula One motor race held on 15 May 2016 at the Circuit de Barcelona-Catalunya in Montmeló, Spain. The race was the fifth round of the 2016 FIA Formula One World Championship, and marked the forty-sixth running of the Spanish Grand Prix as a round of the Formula One World Championship. It was the twenty-sixth time that the race has been held at the circuit. (Full article...) -
Image 21The Moorish Castle's Tower of Homage, the largest surviving remnant of Moorish Gibraltar. The dents in its eastern wall were caused by Castilian siege engines in 1333.
The history of Moorish Gibraltar began with the landing of the Muslims in Hispania and the fall of the Visigothic Kingdom of Toledo in 711 and ended with the fall of Gibraltar to Christian hands 751 years later, in 1462, with an interregnum during the early 14th century. (Full article...) -
Image 22
Teresa Mañé i Miravet (1865–1939), also known by her pen name Soledad Gustavo, was a Catalan teacher, editor and writer. As a proponent of progressive education, Mañé founded some of the first secular schools in Catalonia. With her husband Joan Montseny, she edited the magazine La Revista Blanca, in which she elaborated her ideas on anarchism, feminism and pedagogy. Her daughter Frederica Montseny i Mañé went on to become a leading figure in the Spanish anarchist movement and the Minister of Health of the Second Spanish Republic. (Full article...) -
Image 23
Léon Joseph Marie Ignace Degrelle (French: [dəgʁɛl]; 15 June 1906 – 31 March 1994) was a Belgian Walloon politician and Nazi collaborator. He rose to prominence in Belgium in the 1930s as the leader of the Rexist Party (Rex). During the German occupation of Belgium during World War II, he enlisted in the German army and fought in the Walloon Legion on the Eastern Front. After the collapse of the Nazi regime, Degrelle escaped and went into exile in Francoist Spain, where he remained a prominent figure in neo-Nazi politics. (Full article...) -
Image 24
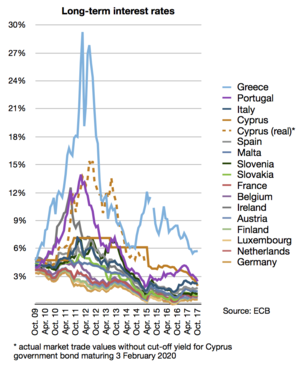
Long-term interest rates (secondary market yields of government bonds with maturities of close to ten years) of all eurozone countries except Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania. A yield being more than 4% points higher compared to the lowest comparable yield among the eurozone states, i.e. yields above 6% in September 2011, indicates that financial institutions have serious doubts about credit-worthiness of the state.
The European debt crisis, often also referred to as the eurozone crisis or the European sovereign debt crisis, was a multi-year debt crisis that took place in the European Union (EU) from 2009 until the mid to late 2010s. Several eurozone member states (Greece, Portugal, Ireland, Spain, and Cyprus) were unable to repay or refinance their government debt or to bail out over-indebted banks under their national supervision without the assistance of third parties like other eurozone countries, the European Central Bank (ECB), or the International Monetary Fund (IMF). (Full article...) -
Image 25Costa with Chelsea F.C. in 2015
Diego da Silva Costa (Spanish: [ˈdjeɣo ða ˈsilβa ˈkosta], Portuguese: [ˈdʒjeɡu dɐ ˈsiwvɐ ˈkɔstɐ]; born 7 October 1988) is a professional footballer who plays as a striker for Campeonato Brasileiro Série A club Grêmio. (Full article...)
General images
-
Image 3The Port of Seville in the late 16th century. Seville became one of the most populous and cosmopolitan European cities after the expeditions to the New World. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 5El paseo de las Delicias, a 1784–1785 painting by Ramón Bayeu depicting a meeting of members of the aristocracy in the aforementioned location. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 9People's militias attacking on a Rebel position in Somosierra in the early stages of the war. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 101894 satirical cartoon depicting the tacit accord for seamless government change (turnismo) between the leaders of two dynastic parties (Sagasta and Cánovas del Castillo), with the country being lied in an allegorical fashion. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 12The explosion of the USS Maine launched the Spanish–American War in April 1898 (from History of Spain)
-
Image 13Recognition of the Duke of Anjou as King of Spain, under the name of Philip V , November 16, 1700 (from History of Spain)
-
Image 14Plaza Mayor with the Casa de la Panadería to the left (from Spanish Golden Age)
-
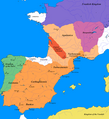
Image 15The Christian kingdoms of Hispania and the Islamic Almohad empire c. 1210
-
Image 16Members of the provisional government after the 1868 Glorious Revolution, by Jean Laurent. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 17Wedding portrait of the Catholic Monarchs (from History of Spain)
-
Image 18The pro-independence forces delivered a crushing defeat to the royalists and secured the independence of Peru in the 1824 battle of Ayacucho. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 19Two women and a man during the siege of the Alcázar (from History of Spain)
-
Image 20The promulgation of the Constitution of 1812, oil painting by Salvador Viniegra. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 21Las Meninas (1656, English: The Maids of Honour) by Diego Velázquez (from Spanish Golden Age)
-
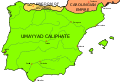
Image 22Visigothic Hispania and its regional divisions in 700, prior to the Muslim conquest (from History of Spain)
-
Image 26The successful 1925 Alhucemas landing turned the luck in the Rif War towards Spain's favour. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 27The Iberian Peninsula in the 3rd century BC (from History of Spain)
-
Image 31Map of territories that were once part of the Spanish Empire (from History of Spain)
-
Image 33Illustration depicting the (now lost) Luzaga's Bronze, an example of the Celtiberian script. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 34Francisco Franco and his appointed successor Prince Juan Carlos de Borbón. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 36The Second of May 1808 was the beginning of the popular Spanish resistance against Napoleon. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 38Felipe González signing the treaty of accession to the European Economic Community on 12 June 1985. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 42Celebrations of the proclamation of the 2nd Republic in Barcelona. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 46The Conquest of Tenochtitlán (from History of Spain)
-
Image 47The greatest extent of the Visigothic Kingdom of Toulouse, c. 500, showing Territory lost after Vouillé in light orange (from History of Spain)
-
Image 49Visigothic King Roderic haranguing his troops before the Battle of Guadalete (from History of Spain)
-
Image 50Louis XIV of France and Philip IV of Spain at the Meeting on the Isle of Pheasants in June 1660, part of the process to put an end to the Franco-Spanish War (1635–59). (from History of Spain)
-
Image 54Christopher Columbus leads expedition to the New World, 1492, sponsored by Spanish crown (from History of Spain)
-
Image 55Episode of the 1854 Spanish Revolution in the Puerta del Sol, by Eugenio Lucas Velázquez. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 56The title page of the Gramática de la lengua castellana (1492), the first grammar of a modern European language to be published. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 57Execution of Torrijos and his men in 1831. Ferdinand VII took repressive measures against the liberal forces in his country. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 58Ethnology of the Iberian Peninsula c. 200 BC (from History of Spain)
-
Image 59Charles I of Spain (better known in the English-speaking world as the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V) was the most powerful European monarch of his day. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 62The realms of Philip II of SpainTerritories administered by the Council of CastileTerritories administered by the Council of AragonTerritories administered by the Council of PortugalTerritories administered by the Council of ItalyTerritories administered by the Council of the IndiesTerritories appointed to the Council of Flanders(from Spanish Golden Age)
-
Image 63Panoramic view of the lower level patio of the Palace (from Spanish Golden Age)
-
Image 64Cabeza de Luis Buñuel, sculptor's work by Iñaki, in the center Buñuel Calanda. (from Culture of Spain)
-
Image 67In ictu oculi ("In the blink of an eye"), a vanitas by Juan de Valdés Leal (from Spanish Golden Age)
-
Image 68Proclamation of the Spanish Republic in Madrid (from History of Spain)
-
Image 69Detail of the votive crown of Recceswinth from the Treasure of Guarrazar, (Toledo-Spain) hanging in Madrid. The hanging letters spell [R]ECCESVINTHVS REX OFFERET [King R. offers this]. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 70Visigothic church, San Pedro de la Nave. Zamora. Spain (from History of Spain)
In the news
- 31 July 2024 – Human trafficking in Spain
- Twenty-six people are arrested by Spanish police in Madrid, Málaga, and Toledo for operating a sex trafficking ring that abused over 600 women. 32 women were freed during the operation. (AP)
- 30 July 2024 –
- Spain's competition watchdog fines online travel agency Booking.com with a record €413 million fine for "abusing its dominant position" in the past five years. (France 24)
- 27 July 2024 – 2024 UEFA Women's Under-19 Championship
- In association football, Spain defeats the Netherlands 2–1 in the final to win their sixth UEFA Women's Under-19 Championship title. (UEFA)
- 25 July 2024 – Spanish General Council of the Judiciary blockade
- The twenty new members of the General Council of the Judiciary are sworn in, putting an end to the institutional crisis that the country's supreme judicial administrative body experienced for five years. (RTVE)
- 31 July 2024 – Human trafficking in Spain
- Twenty-six people are arrested by Spanish police in Madrid, Málaga, and Toledo for operating a sex trafficking ring that abused over 600 women. 32 women were freed during the operation. (AP)
Spain topics
Categories
WikiProjects
- Main project
WikiProject Spain
- Related projects
WikiProject Basque • WikiProject Catalan-speaking Countries • WikiProject Galicia • Spanish Translation of the Week
Things you can do

- Add {{WikiProject Spain}} to article talk pages which have some relation to Spain
- Help write new Spain-related articles and improve and expand existent ones
- Assess: unassessed Spain-related articles
- Suggest: selected articles, biographies, pictures, did you knows? and quotes for this Portal
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
-
List of all portals
-

-

-

-

-
WikiProject Portals
- ^ "Atlantic hurricane best track (HURDAT version 2)" (Database). United States National Hurricane Center. April 5, 2023. Retrieved August 2, 2024.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This page was last updated at 2024-08-02 10:00 UTC. Update now. View original page.
All our content comes from Wikipedia and under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License.





























































































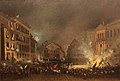













![Image 69Detail of the votive crown of Recceswinth from the Treasure of Guarrazar, (Toledo-Spain) hanging in Madrid. The hanging letters spell [R]ECCESVINTHVS REX OFFERET [King R. offers this]. (from History of Spain)](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/f2/Corona_de_%2829049230050%29.jpg/57px-Corona_de_%2829049230050%29.jpg)


















